If you’ve come across the terms @googlemail.com and @gmail.com and wondered how they relate to your email account, you’re not alone. Here’s the good news: both email domains are fully interchangeable. You can use either without any issues.
But why are there two domains? And what does this mean for your email experience? Let’s break it down.
The Story Behind Googlemail
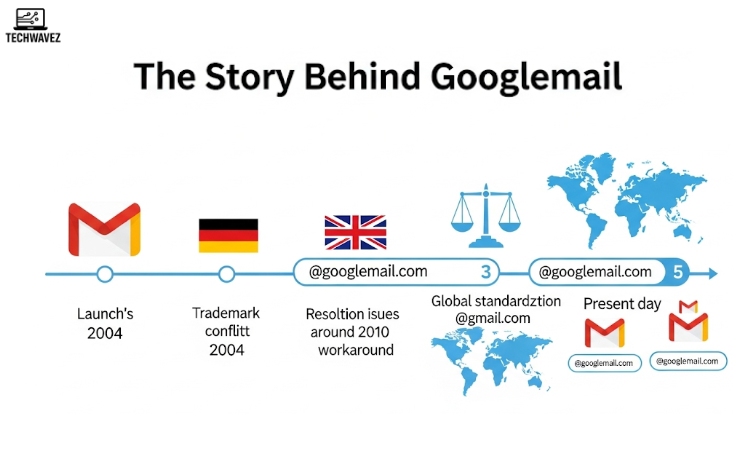
To understand the difference, we need to go back to Gmail’s early days.
When Gmail launched in 2004, it quickly became popular across the globe. However, in certain countries like Germany and the UK, the name “Gmail” was already trademarked by other companies. Because of this, Google couldn’t offer “@gmail.com” addresses in those regions initially.
As a workaround, they provided users with email addresses ending in @googlemail.com instead. So, if you signed up for Gmail in Germany in 2005, your address probably looked like yourname@googlemail.com.
Eventually, Google resolved these legal issues, and by 2010, “@gmail.com” became the global standard. Still, many users kept their original “@googlemail.com” addresses — and both domains continue to function to this day.
How Gmail and Googlemail Work

Here’s what really matters: both @gmail.com and @googlemail.com point to the same email account.
For example:
- Emails sent to johnsmith@gmail.com will also reach johnsmith@googlemail.com.
- If you signed up for an app or service with @googlemail.com, you can still log in using @gmail.com, and vice versa.
Google automatically routes emails sent to either domain to the same inbox. Think of it like having two different doorbells — but they both ring the same house.
What This Means for You
1. Easy Email Sharing
You don’t have to worry about which version of your email you’re using. Whether it ends in @gmail.com or @googlemail.com, they both work perfectly. Just use the one you prefer.
2. Flexibility During Account Creation
Some websites auto-fill “@gmail.com” when you enter an email. If your original address is @googlemail.com, no problem — it’s still recognized as the same account.
Likewise, if your login was originally set up with @googlemail.com, you can usually log in using @gmail.com instead.
3. One Account, Not Two
There’s no duplication. Both addresses lead to one inbox, one Google account, and all your emails, settings, and filters remain the same.
A Smooth Experience for Users
One of Gmail’s strengths is its simplicity. Google ensures a smooth, hassle-free experience — even with two domains in play.
Even when you set up filters or create labels, Gmail recognizes both domains. For instance, if you create a filter for messages sent to “@gmail.com”, it will automatically catch ones sent to “@googlemail.com” too.
No Security Difference
You might wonder if one domain is more secure than the other. The answer is simple: both are equally secure.
Whether you use @gmail.com or @googlemail.com, your account benefits from:
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
- Advanced spam protection
- Encryption and security monitoring
Google’s best-in-class security applies equally to both domains, so you’re protected either way.
Final Thoughts
Here’s a quick summary:
- Both @gmail.com and @googlemail.com work the same.
- You don’t need to update or change your email.
- There’s no impact on security, filters, or login.
- You can choose whichever domain feels right for you.
Want a deeper dive into the difference between Gmail and Googlemail?
Read the full guide here:
Difference Between Gmail and Googlemail