Have you ever thought about how fit you really are? A weighing scale can tell you your body weight, but that alone doesn’t paint the full picture of your health. That’s where BMI, or Body Mass Index, becomes helpful. It’s a quick way to understand whether you’re underweight, at a healthy weight, overweight, or obese.
Now imagine having a tool that calculates your BMI—and you built it yourself with code. Pretty cool, right?
In this guide, you’ll learn how to create a simple BMI calculator using Python functions. We’ll walk through the logic, show you the complete code, and even give ideas for improving it further. Whether you’re new to coding or brushing up on Python, this is a great project to get started.
What Is BMI?
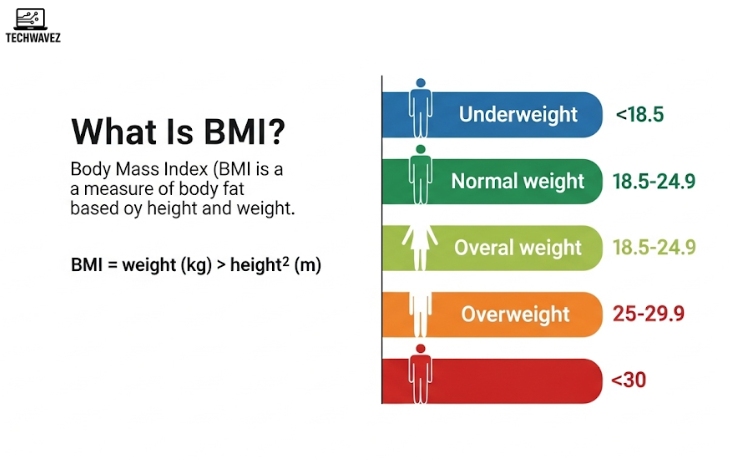
BMI stands for Body Mass Index. It estimates your body fat based on two simple inputs: weight and height.
The formula is:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²)
Here’s how the results are generally categorized:
- Underweight: BMI < 18.5
- Normal weight: 18.5 ≤ BMI < 25
- Overweight: 25 ≤ BMI < 30
- Obese: BMI ≥ 30
For example, if you weigh 68 kg and are 1.65 meters tall:
BMI = 68 ÷ (1.65²) ≈ 24.98
Your BMI would fall into the “Normal weight” category.
Step 1: Setting Up Your Python Environment

Before coding, make sure you have Python installed.
If you’re new:
- Download Python from python.org.
- You can use built-in tools like IDLE, or install an editor like VS Code or PyCharm.
- Test your setup by opening a new file and running:
print("Hello, world!")
Once that works, you’re ready to code your BMI calculator.
Step 2: Creating the BMI Calculator
We’ll build this program using two Python functions:
calculate_bmi()– This performs the actual calculation.interpret_bmi()– This categorizes the result.
Define calculate_bmi():
def calculate_bmi(weight, height):
"""
Calculate BMI using the formula: weight / height^2
Args:
- weight (float): weight in kilograms
- height (float): height in meters
Returns:
- float: the BMI value
"""
return weight / (height ** 2)
Define interpret_bmi():
def interpret_bmi(bmi):
"""
Categorize the BMI result.
Args:
- bmi (float): the calculated BMI
Returns:
- str: the BMI category
"""
if bmi < 18.5:
return "Underweight"
elif 18.5 <= bmi < 25:
return "Normal weight"
elif 25 <= bmi < 30:
return "Overweight"
else:
return "Obese"
Step 3: Putting It All Together
Now we’ll combine both functions and add user input.
Here’s the complete program:
def calculate_bmi(weight, height):
return weight / (height ** 2)
def interpret_bmi(bmi):
if bmi < 18.5:
return "Underweight"
elif 18.5 <= bmi < 25:
return "Normal weight"
elif 25 <= bmi < 30:
return "Overweight"
else:
return "Obese"
def main():
print("Welcome to the BMI Calculator!")
try:
weight = float(input("Enter your weight in kilograms (e.g., 70): "))
height = float(input("Enter your height in meters (e.g., 1.75): "))
bmi = calculate_bmi(weight, height)
category = interpret_bmi(bmi)
print(f"\nYour BMI is {bmi:.2f}. This is considered '{category}'.")
except ValueError:
print("Invalid input. Please enter numeric values for weight and height.")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Example Output:
Input:
Weight = 68 kg, Height = 1.65 m
Output:Your BMI is 24.98. This is considered 'Normal weight'.
Enhancing Your BMI Calculator
Want to take it further? Try these upgrades:
- Error Handling: Prevent crashes if users enter invalid data.
- Unit Conversion: Accept weight in pounds or height in inches, then convert to metric.
- GUI Support: Use Python libraries like
TkinterorPyQtto create a user-friendly interface. - Add Health Tips: Offer basic fitness advice based on the BMI result.
If you enjoy learning through projects, you might also like this tutorial on how to reset your YouTube video recommendations—it’s perfect for cleaning up your content feed using simple actions.
Learn More
To build more tools like this, check out:
The more you practice, the easier it gets.
Start Building Your Own Tools
You’ve just built a working Python app. That’s no small thing!
Through this tutorial, you learned:
- What BMI is and why it’s useful.
- How to set up your Python environment.
- How to build and run a simple program using functions.
From here, you can try creating other practical tools like a calorie tracker, a savings calculator, or even a daily habit tracker.
With Python, your ideas can come to life—line by line.